Mycobacterium Tuberculosis INH Resistance
Product Name
HWTS-RT002A-Mycobacterium Tuberculosis INH Detection Kit (Fluorescence PCR)
Certificate
Myanmar FDA
Epidemiology
Isoniazid, a key anti-tuberculosis drug introduced in 1952, is one of the most effective drugs for combined treatment of active tuberculosis and a single drug for latent tuberculosis.
KatG is the main gene encoding catalase-peroxidase and katG gene mutation can promote the synthesis of mycolic acid cell wall, making the bacteria resistant to isoniazid. KatG expression is negatively correlated with changes in INH-MIC, and a 2-fold decrease in katG expression results in a slightly larger 2-fold increase in MIC. Another cause of isoniazid resistance in mycobacterium tuberculosis occurs when base insertion, deletion or mutation occurs in the InhA gene locus of mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Channel
| ROX | inhA (-15C>T) site· |
| CY5 |
katG (315G>C) site |
| VIC (HEX) |
IS6110 |
Technical Parameters
| Storage | ≤-18℃ In dark |
| Shelf-life |
12 months |
| Specimen Type |
Sputum |
| CV | ≤5.0% |
| LoD |
1 × 103 bacteria/mL |
| Specificity |
No-cross reactivity with the mutations of the four drug resistance sites (511, 516, 526 and 531) of the rpoB gene outside the detection range of the detection kit. |
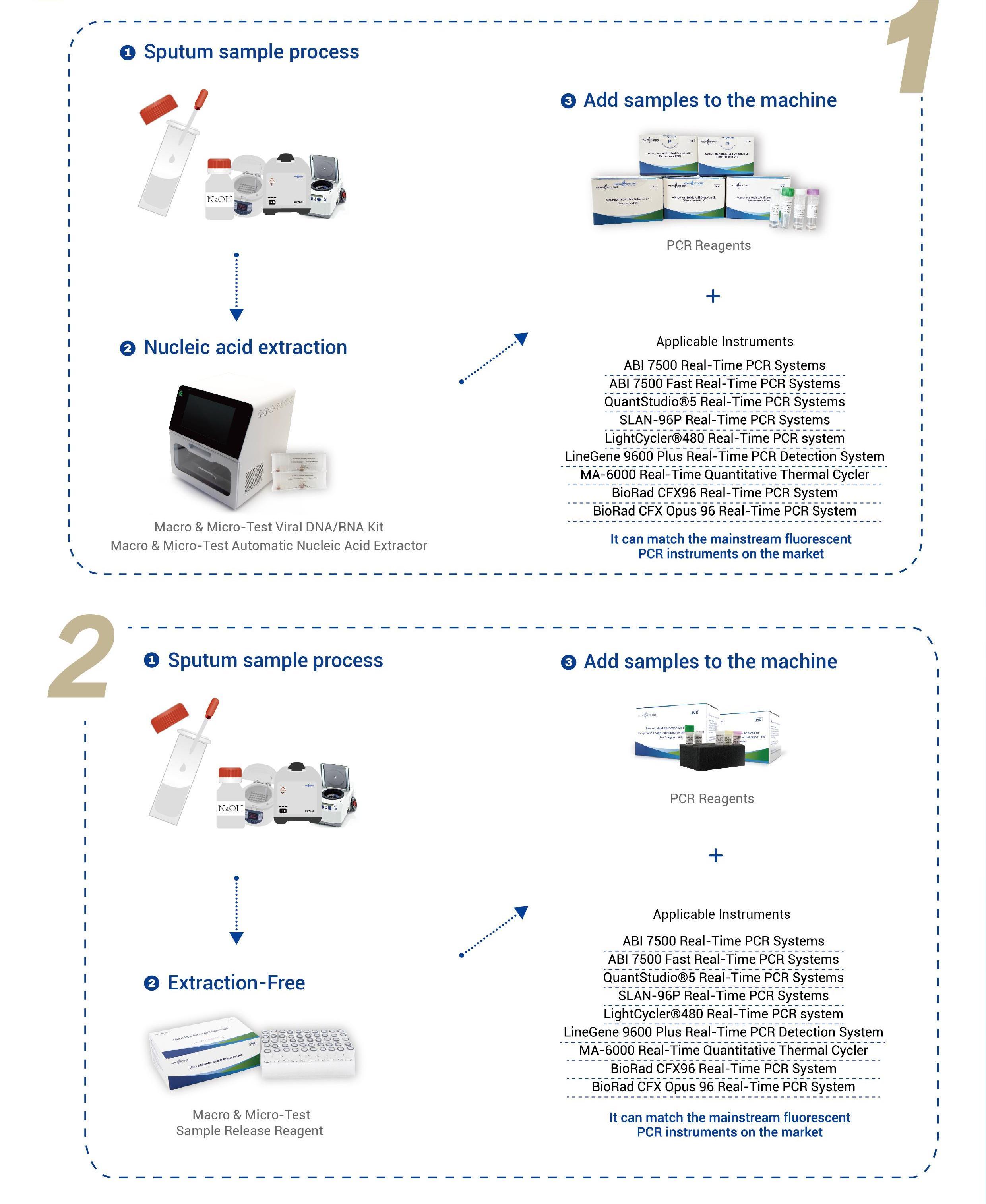
| Applicable Instruments |
Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR Systems Applied Biosystems 7500 Fast Real-Time PCR Systems QuantStudio®5 Real-Time PCR Systems SLAN-96P Real-Time PCR Systems LightCycler®480 Real-Time PCR system LineGene 9600 Plus Real-Time PCR Detection System MA-6000 Real-Time Quantitative Thermal Cycler BioRad CFX96 Real-Time PCR System BioRad CFX Opus 96 Real-Time PCR System |