October 20th is World Osteoporosis Day every year.
Calcium loss, bones for help, World Osteoporosis Day teaches you how to care!
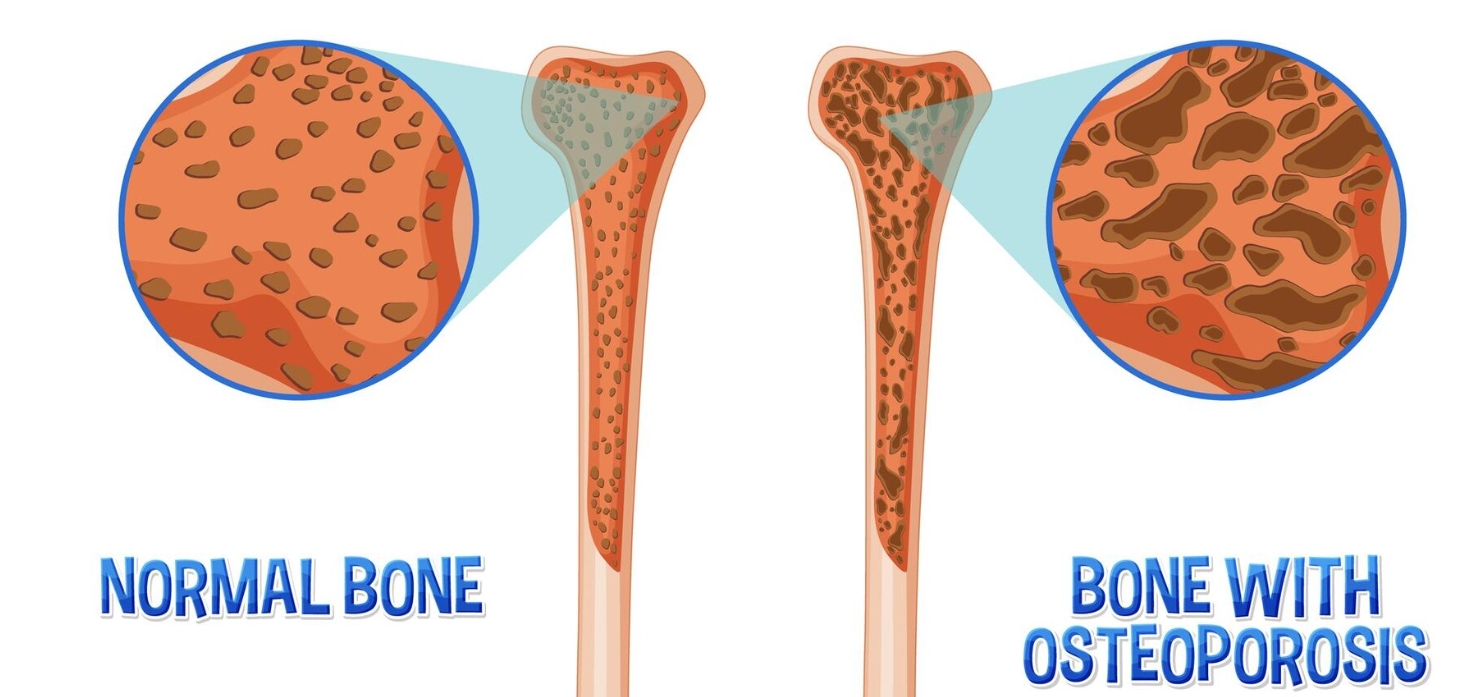
01 Understanding osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is the most common systemic bone disease. It is a systemic disease characterized by decreasing bone mass, destroying bone microstructure, increasing bone brittleness and prone to fracture. More common in postmenopausal women and elderly men.
Main features
- Low back pain
- Spinal deformation (such as hunchback, spinal deformation, elevation and shortening)
- Low bone mineral content
- Be prone to fracture
- Destruction of bone structure
- Decreased bone strength
The three most common symptoms
Pain-low back pain, fatigue or bone pain all over the body, often diffuse, without fixed parts. Fatigue is often aggravated after fatigue or activity.
Humpback-spinal deformity, shortened figure, common vertebral compression fracture, and serious spinal deformity such as humpback.
Fracture-brittle fracture, which occurs when a slight external force is applied. The most common sites are spine, neck and forearm.
High-risk population of osteoporosis
- old age
- Female menopause
- Maternal family history (especially hip fracture family history)
- Low weight
- smoke
- Hypogonadism
- Excessive drinking or coffee
- Less physical activity
- Calcium and/or vitamin D deficiency in diet (less light or less intake)
- Diseases affecting bone metabolism
- Application of drugs affecting bone metabolism
02 Harm of osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is called the silent killer. Fracture is a serious consequence of osteoporosis, and it is often the first symptom and the reason for seeing a doctor in some patients with osteoporosis.
Pain itself can reduce the quality of life of patients.
Deformities and fractures of the spine can cause disability.
Causing heavy family and social burdens.
Osteoporotic fracture is one of the main causes of disability and death in elderly patients.
20% of patients will die of various complications within one year after the fracture, and about 50% of patients will be disabled.
03 How to prevent osteoporosis
The mineral content in human bones reaches the highest in their thirties, which is called peak bone mass in medicine. The higher the peak bone mass, the more the "bone mineral bank" reserves in the human body, and the later the onset of osteoporosis in the elderly, the lighter the degree.
People at all ages should pay attention to the prevention of osteoporosis, and the lifestyle of infants and young people is closely related to the occurrence of osteoporosis.
After old age, actively improving diet and lifestyle and insisting on calcium and vitamin D supplementation can prevent or alleviate osteoporosis.
balanced diet
Increase the intake of calcium and protein in the diet, and adopt a low-salt diet.
Calcium intake plays an irreplaceable role in preventing osteoporosis.
Reduce or eliminate tobacco, alcohol, carbonated drinks, espresso and other foods that affect bone metabolism.
Moderate exercise
The human bone tissue is a living tissue, and the muscle activity in exercise will constantly stimulate the bone tissue and make the bone stronger.
Exercise helps to enhance the body's responsiveness, improve the balance function and reduce the risk of falling.
Increase sunlight exposure
China people's diet contains very limited vitamin D, and a large amount of vitamin D3 is synthesized by skin exposed to sunlight and ultraviolet rays.
Regular exposure to sunlight will play a key role in the production of vitamin D and calcium absorption.
Normal people get at least 20 minutes of sunshine every day, especially in winter.
Osteoporosis solution
In view of this, the 25-hydroxyvitamin D detection kit developed by Hongwei TES provides solutions for the diagnosis, treatment monitoring and prognosis of bone metabolism:
25-Hydroxyvitamin D(25-OH-VD) determination kit (fluorescence immunochromatography)
Vitamin D is an essential substance for human health, growth and development, and its deficiency or excess is closely related to many diseases, such as musculoskeletal diseases, respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, immune diseases, kidney diseases, neuropsychiatric diseases and so on.
25-OH-VD is the main storage form of vitamin D, accounting for more than 95% of the total VD. Because it has a half-life (2~3 weeks) and is not affected by blood calcium and thyroid hormone levels, it is recognized as a marker of vitamin D nutritional level.
Sample type: serum, plasma and whole blood samples.
LoD:≤3ng/mL
Post time: Oct-24-2023