At the end of 1995, the World Health Organization (WHO) designated March 24th as the World Tuberculosis Day.
1 Understanding tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is a chronic consumptive disease, also called "consumption disease". It is a highly contagious chronic consumptive disease caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis invading human body. It is not affected by age, sex, race, occupation and region. Many organs and systems of human body can suffer from tuberculosis, among which tuberculosis is the most common.
Tuberculosis is a chronic infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which invades the organs of the whole body. Because the common infection site is the lung, it is often called tuberculosis.
More than 90% of the infection of tuberculosis is transmitted through the respiratory tract. Tuberculosis patients are infected by coughing, sneezing, making loud noises, causing droplets with tuberculosis (medically called microdroplets) to be ejected from the body and inhaled by healthy people.
2 Treatment of tuberculosis patients
Drug treatment is the cornerstone of tuberculosis treatment. Compared with other types of bacterial infections, tuberculosis treatment may take longer. For active pulmonary tuberculosis, anti-tuberculosis drugs must be taken for at least 6 to 9 months. The specific drugs and treatment time depend on the patient's age, overall health and drug resistance.
When patients are resistant to first-line drugs, they must be replaced by second-line drugs. The most commonly used drugs for the treatment of non-drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis include isoniazid (INH), rifampicin (RFP), ethambutol (EB), pyrazinamide (PZA) and streptomycin (SM). These five drugs are called first-line drugs and are effective for more than 80% of newly infected pulmonary tuberculosis patients.
3 Tuberculosis question and answer
Q: Can tuberculosis be cured?
A: 90% of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis can be cured after they insist on regular medication and complete the prescribed course of treatment (6-9 months). Any change in treatment should be decided by the doctor. If you don't take the medicine on time and complete the course of treatment, it will easily lead to drug resistance of tuberculosis. Once drug resistance occurs, the course of treatment will be prolonged and it will easily lead to treatment failure.
Q: What should tuberculosis patients pay attention to during treatment?
A: Once you are diagnosed with tuberculosis, you should receive regular anti-tuberculosis treatment as soon as possible, follow the doctor's advice, take medicine on time, check regularly and build up confidence. 1. Pay attention to rest and strengthen nutrition; 2. Pay attention to personal hygiene, and cover your mouth and nose with paper towels when coughing or sneezing; 3. Minimize going out and wear a mask when you have to go out.
Q: Is tuberculosis still contagious after being cured?
A: After standardized treatment, the infectivity of pulmonary tuberculosis patients usually decreases rapidly. After several weeks of treatment, the number of tuberculosis bacteria in sputum will be significantly reduced. Most patients with non-infectious pulmonary tuberculosis complete the whole course of treatment according to the prescribed treatment plan. After reaching the cure standard, no tuberculosis bacteria can be found in sputum, so they are no longer contagious.
Q: Is tuberculosis still contagious after being cured?
A: After standardized treatment, the infectivity of pulmonary tuberculosis patients usually decreases rapidly. After several weeks of treatment, the number of tuberculosis bacteria in sputum will be significantly reduced. Most patients with non-infectious pulmonary tuberculosis complete the whole course of treatment according to the prescribed treatment plan. After reaching the cure standard, no tuberculosis bacteria can be found in sputum, so they are no longer contagious.
Tuberculosis solution
Macro & Micro-Test offers the following products:
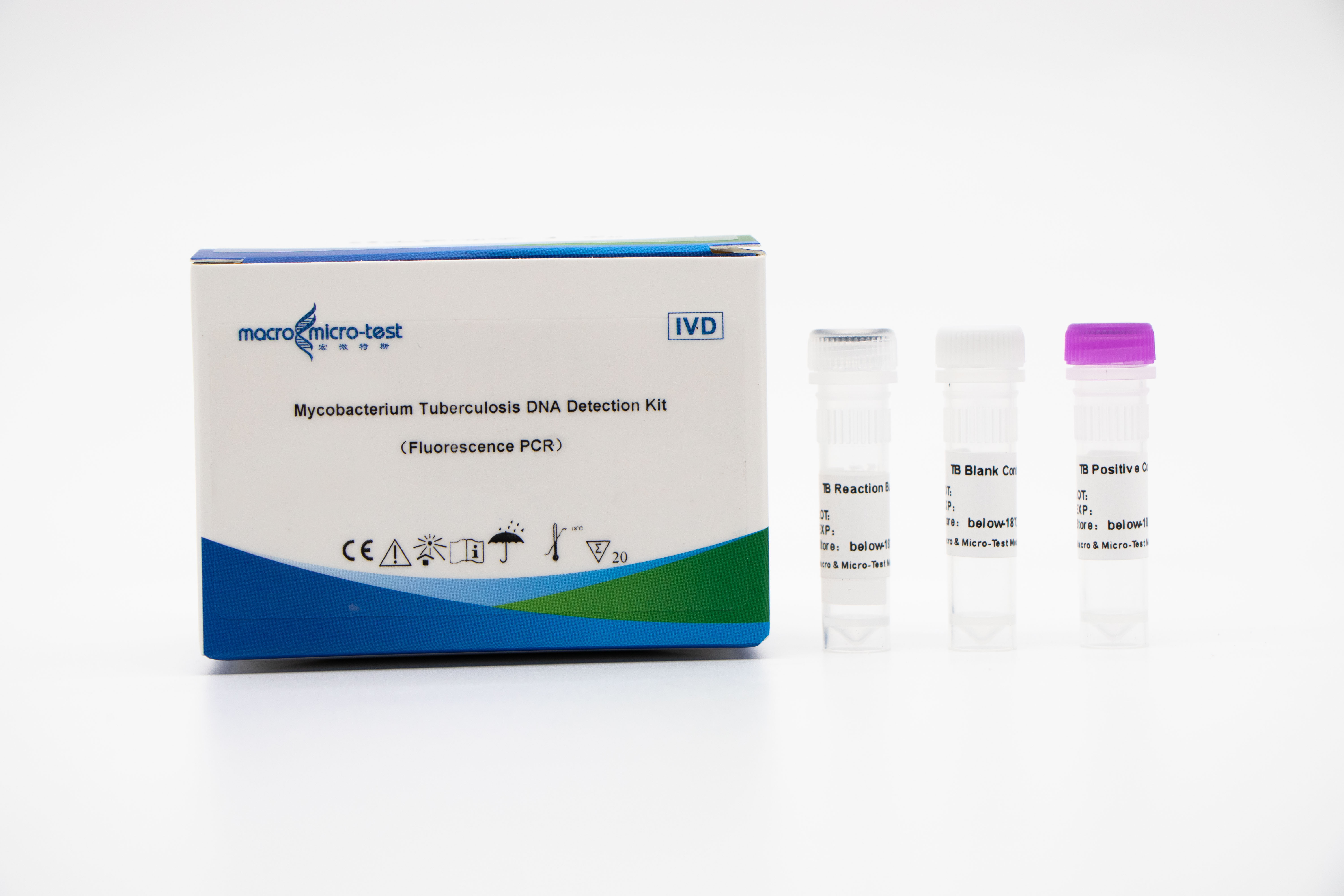
Detection of MTB (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) nucleic acid
1. The introduction of internal reference quality control in the system can comprehensively monitor the experimental process and ensure the experimental quality.
2. PCR amplification and fluorescent probe can be combined.
3. High sensitivity: the minimum detection limit is 1 bacteria /mL.
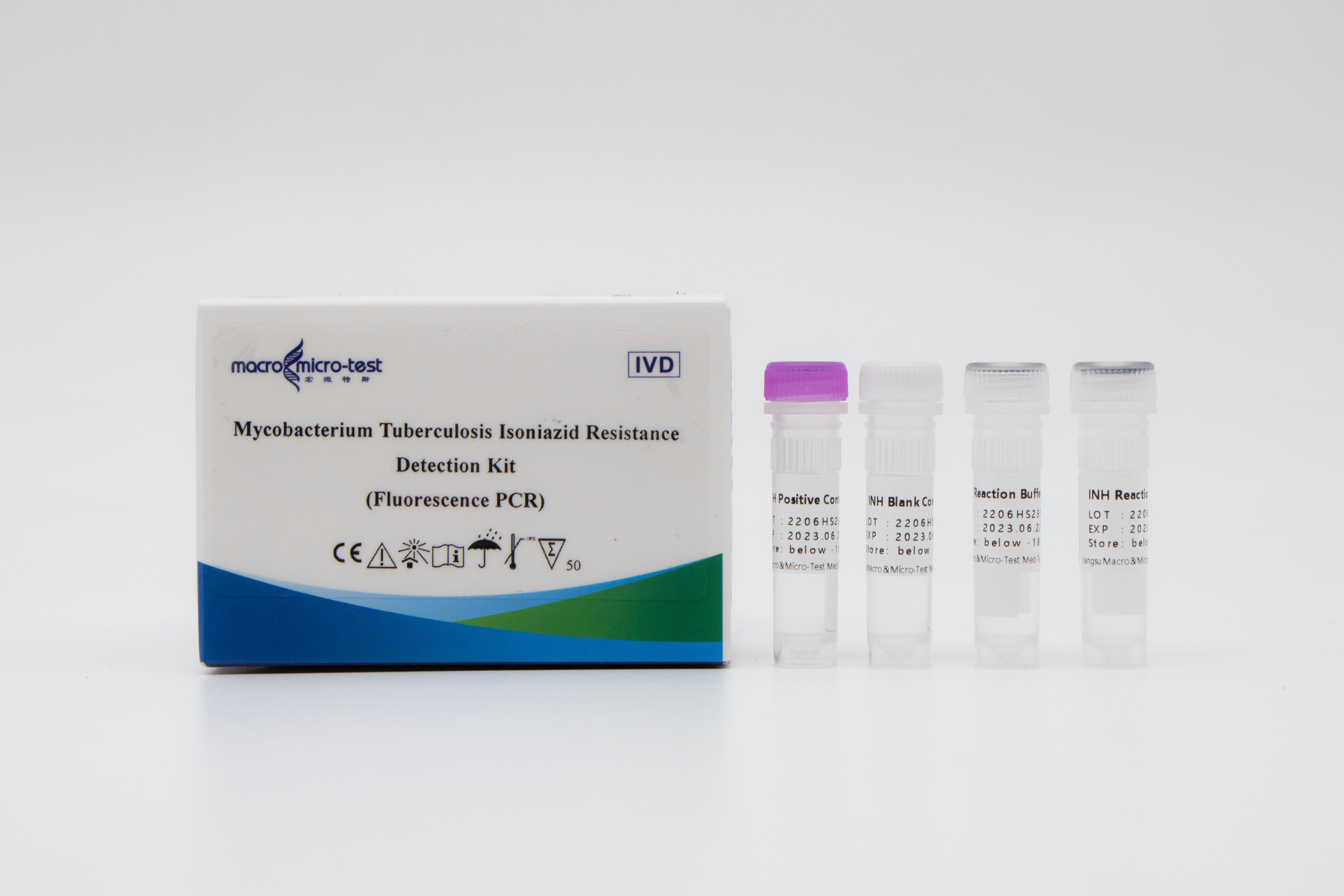
Detection of isoniazid resistance in MTB
1. The introduction of internal reference quality control in the system can comprehensively monitor the experimental process and ensure the experimental quality.
2. A self-improved amplification-blocking mutation system was adopted, and the method of combining ARMS technology with fluorescent probe was adopted.
3. High sensitivity: the minimum detection limit is 1000 bacteria /mL, and the uneven drug-resistant strains with 1% or more mutant strains can be detected.
4. High specificity: There is no cross reaction with the mutations of (511, 516, 526 and 531) four drug resistance sites of rpoB gene.
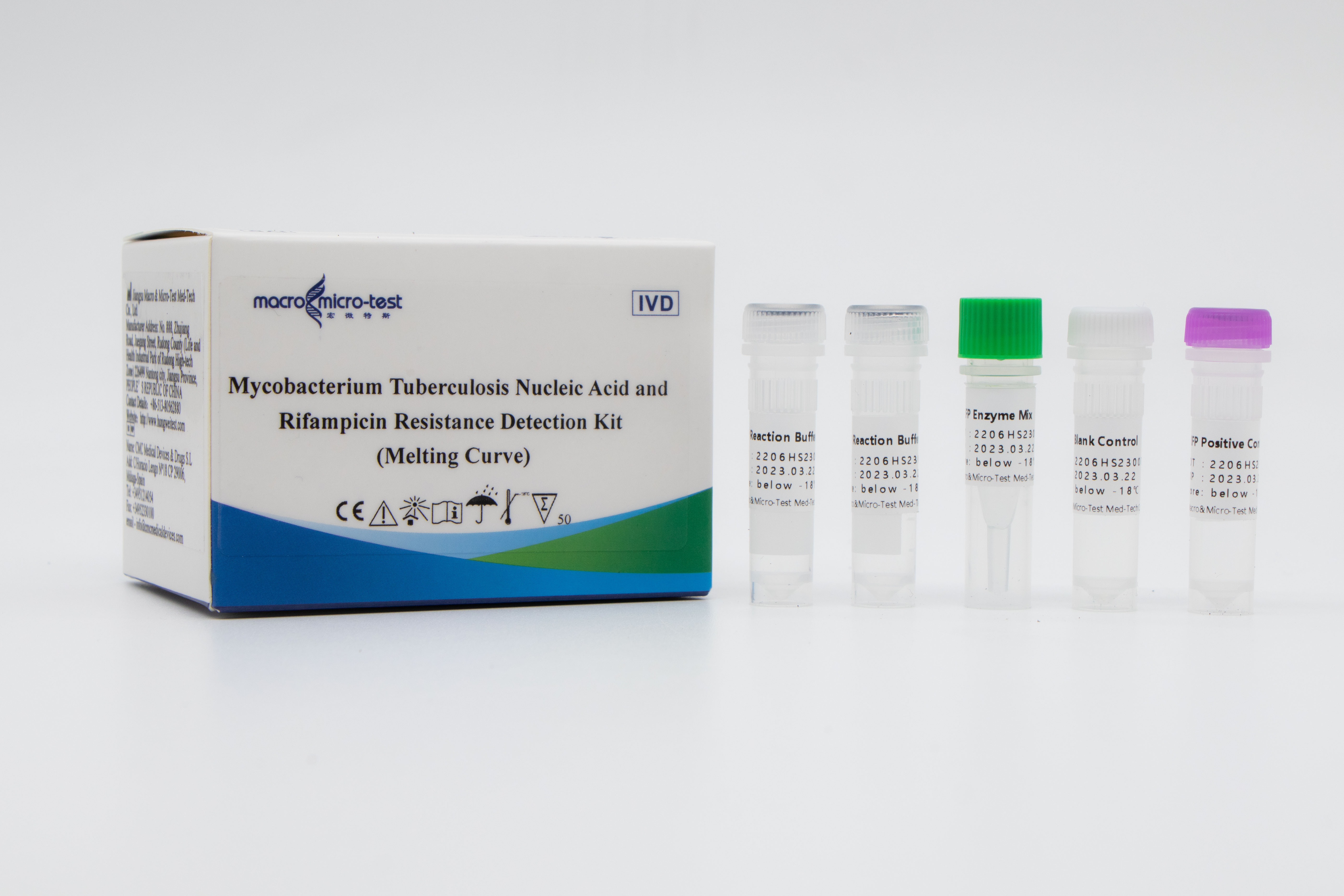
Detection of Mutations of MTB and Rifampicin Resistance
1. The introduction of internal reference quality control in the system can comprehensively monitor the experimental process and ensure the experimental quality.
2. The melting curve method combined with closed fluorescent probe containing RNA bases was used for in vitro amplification detection.
3. High sensitivity: the minimum detection limit is 50 bacteria /mL.
4. High specificity: no cross reaction with human genome, other nontuberculous mycobacteria and pneumonia pathogens; Mutation sites of other drug-resistant genes of wild-type mycobacterium tuberculosis, such as katG 315G>C\A and InhA -15 C>T, were detected, and the results showed no cross reaction.
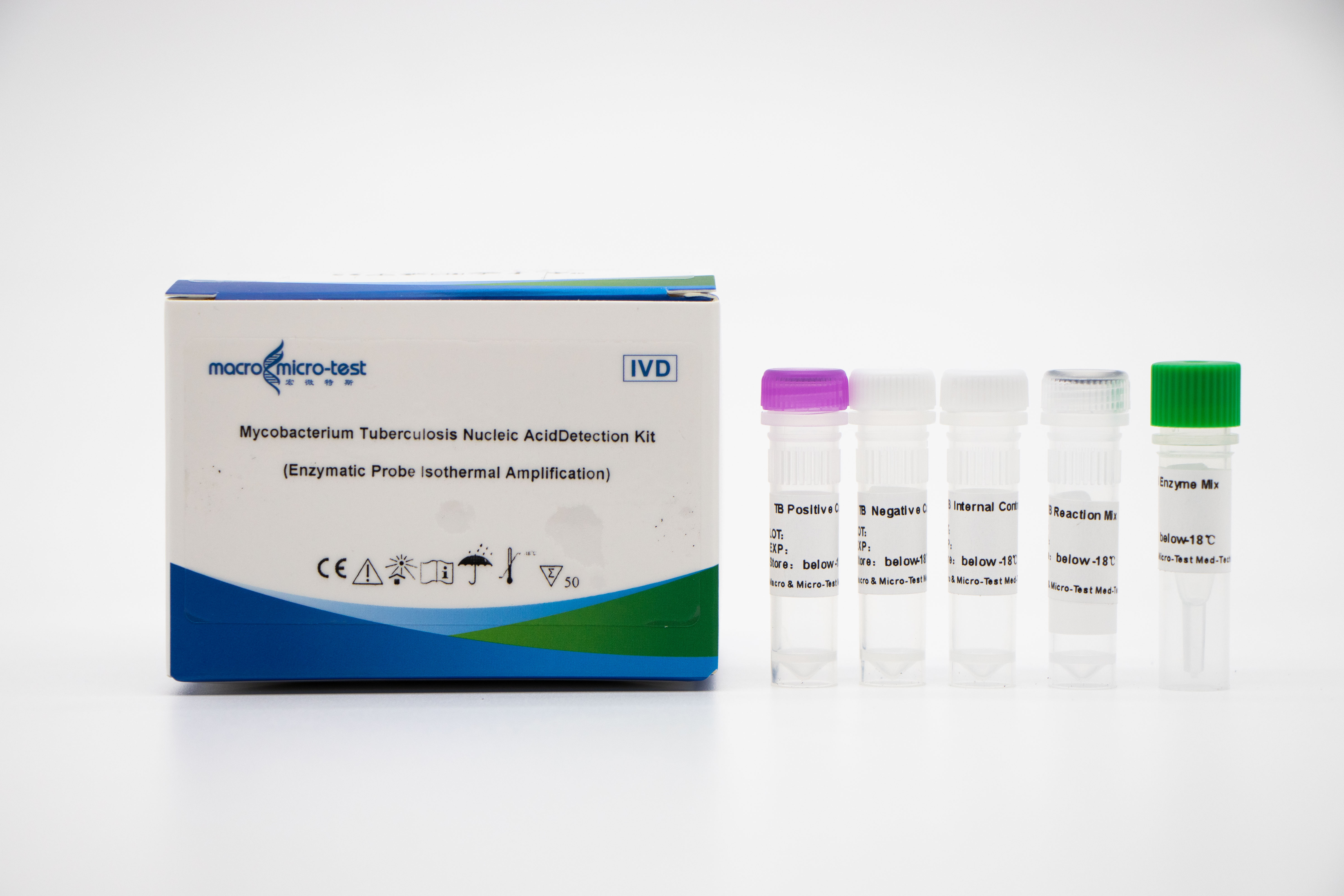
MTB nucleic acid detection (EPIA)
1. The introduction of internal reference quality control in the system can comprehensively monitor the experimental process and ensure the experimental quality.
2. The enzyme digestion probe constant temperature amplification method is adopted, and the detection time is short, and the detection result can be obtained in 30 minutes.
3. Combined with Macro & Micro-Test sample release agent and Macro & Micro-Test constant temperature nucleic acid amplification analyzer, it is easy to operate and suitable for various scenes.
4. High sensitivity: the minimum detection limit is 1000Copies/mL.
5. High specificity: There is no cross reaction with other mycobacteria of non-tuberculosis mycobacteria complex (such as Mycobacterium kansas, Mycobacterium Sukarnica, Mycobacterium marinum, etc.) and other pathogens (such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Escherichia coli, etc.).
Post time: Mar-22-2024